n India, Anganwadi centers play a pivotal role in providing early childhood education, nutrition, and healthcare services to children under the age of six, as well as to pregnant and lactating mothers. These centers serve as a crucial link between communities and government initiatives aimed at improving maternal and child health. However, the effectiveness of Anganwadi centers largely depends on the recruitment of qualified and motivated personnel. In this article, we delve into the significance of Anganwadi recruitment and explore the challenges and opportunities associated with it.
Understanding Anganwadi Centers
Anganwadi centers, established under the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) scheme, serve as the primary platform for delivering essential services related to early childhood care and development. These centers cater to the holistic needs of children by offering early education, supplementary nutrition, immunization, and health check-ups. Additionally, they extend support to women through maternal and reproductive health services, thereby contributing to the overall well-being of families.
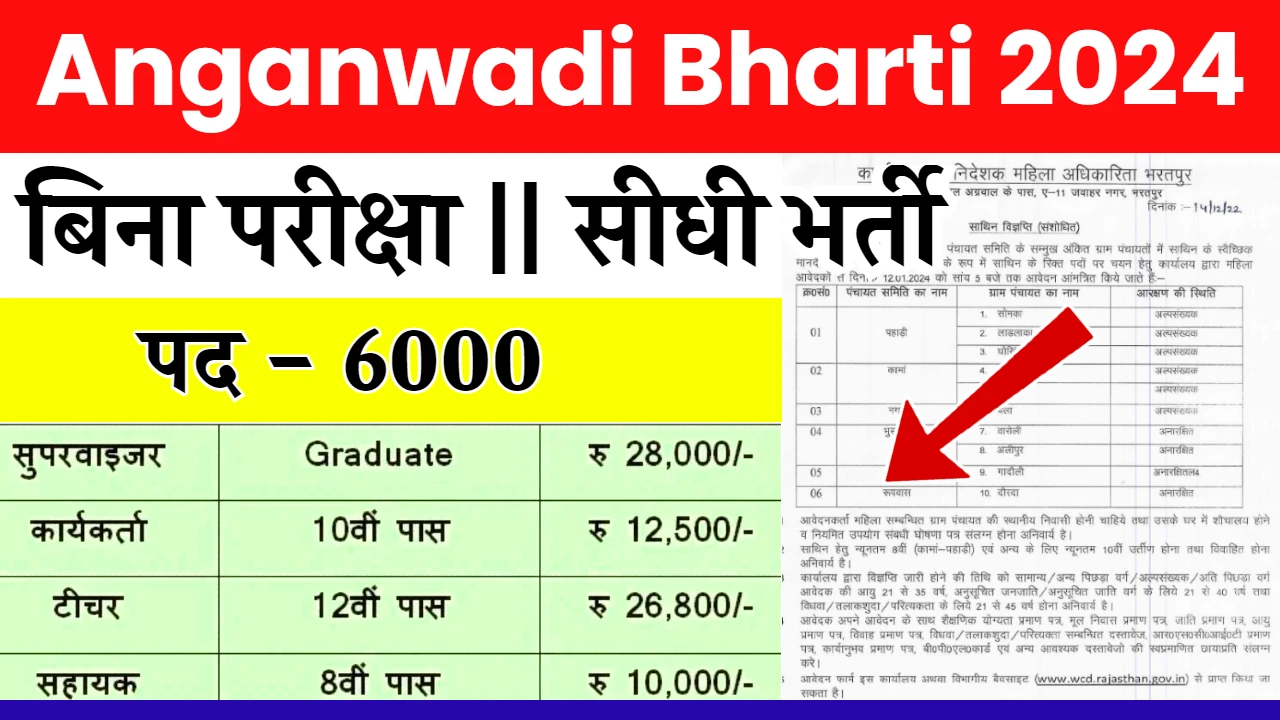
| Name of recruitment | Anganwadi Supervisor Recruitment 2024 |
| Total vacancies | 13,255 Posts |
| Department | Ministry of Women and Child Development |
| Post Name | Anganwadi Supervisor 2024 |
| Application start date | March 2024 |
| Application end date | April 2024 |
| Selection Process | Written Exam & Interview |
| Official Website | https://wcd.nic.in/ |
The Importance of Recruitment
Recruitment is the cornerstone of ensuring the efficacy and efficiency of Anganwadi centers. Qualified personnel, including Anganwadi workers and helpers, are essential for delivering quality services and fostering positive outcomes in child development and maternal health. Effective recruitment practices ensure that individuals with the necessary skills, knowledge, and commitment are selected to serve in these critical roles.
Challenges in Recruitment
Despite the crucial role they play, Anganwadi centers often face challenges in recruiting suitable candidates. Some of the common hurdles include:
Limited Access to Education: In many rural areas where Anganwadi centers are located, access to quality education is limited. This poses a challenge in finding candidates with the required qualifications and training.
Low Remuneration: The remuneration offered to Anganwadi workers and helpers is often inadequate, discouraging qualified candidates from applying for these positions.
Lack of Awareness: There is often a lack of awareness among potential candidates about the opportunities available in Anganwadi centers, leading to a limited pool of applicants.
Gender Disparities: Gender biases and societal norms may restrict the participation of women in the workforce, particularly in certain regions, thereby affecting recruitment efforts.
| Criteria | Details |
| Age Limit | 18 – 35 years |
| Age Relaxation | As per government norms for reserved categories |
| Educational Qualification | Bachelor’s degree from a recognized university |
| Work Experience | May be required for some positions (varies by region) |
| Documents Required | |
| – | Scanned passport-sized photograph |
| – | Scanned signature |
| – | Educational certificates |
| – | Caste certificate (if applicable) |
| – | Domicile certificate (if applicable) |
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
Addressing the challenges in Anganwadi recruitment requires a multi-faceted approach. Some strategies that can be adopted include:
Enhanced Outreach and Awareness: Government agencies and NGOs can collaborate to raise awareness about the benefits of working in Anganwadi centers and the opportunities available for career growth and skill development.
Improving Remuneration and Incentives: Reviewing and revising the remuneration structure to make it more competitive and providing additional incentives such as healthcare benefits and opportunities for further education can make these positions more attractive.
Investing in Training and Capacity Building: Providing comprehensive training and capacity-building programs for Anganwadi workers and helpers can enhance their skills and confidence in delivering quality services.
Promoting Gender Equality: Efforts should be made to challenge gender stereotypes and promote equal opportunities for women in the workforce, thereby encouraging more women to pursue careers in Anganwadi centers.
| State | Number of vacancies |
| Rajasthan Anganwadi Recruitment | 1500 |
| Karnataka Anganwadi Recruitment | 1200 |
| Tamil Nadu Anganwadi Recruitment | 1000 |
| Uttar Pradesh Anganwadi Recruitment | 1200 |
| Maharashtra Anganwadi Recruitment | 800 |
| Jharkhand Anganwadi Recruitment | 800 |
| Assam Anganwadi Recruitment | 700 |
| Punjab Anganwadi Recruitment | 600 |
| Haryana Anganwadi Recruitment | 400 |
| Jammu and Kashmir Anganwadi Recruitment | 300 |
| Uttarakhand Anganwadi Recruitment | 200 |
| Himachal Pradesh Anganwadi Recruitment | 150 |
| Goa Anganwadi Recruitment | 50 |
| Kerala Anganwadi Recruitment | 500 |
| Chhattisgarh Anganwadi Recruitment | 500 |
| Odisha Anganwadi Recruitment | 900 |
| West Bengal Anganwadi Recruitment | 1300 |
| Gujarat Anganwadi Recruitment | 700 |
| Bihar Anganwadi Recruitment | 1100 |
| Madhya Pradesh Anganwadi Recruitment | 1000 |
| Andhra Pradesh Anganwadi Recruitment | 800 |
| Telangana Anganwadi Recruitment | 600 |
| Tripura Anganwadi Recruitment | 100 |
| Manipur Anganwadi Recruitment | 80 |
| Meghalaya Anganwadi Recruitment | 70 |
| Nagaland Anganwadi Recruitment | 60 |
| Arunachal Pradesh Anganwadi Recruitment | 40 |
| Mizoram Anganwadi Recruitment | 30 |
| Sikkim Anganwadi Recruitment | 20 |
| Andaman and Nicobar Anganwadi Recruitment | 10 |
| Total vacancies | 12000 |
Conclusion
Anganwadi recruitment is a critical aspect of ensuring the effectiveness and sustainability of early childhood development programs in India. By addressing the challenges associated with recruitment and implementing strategies to attract and retain qualified personnel, we can strengthen Anganwadi centers’ capacity to provide essential services to children and women, thereby contributing to the nation’s overall health and well-being. Through concerted efforts and collaborative initiatives, we can bridge the gaps in Anganwadi recruitment and create a brighter future for generations to come.




